According to Albert Einstein’s law on the equivalence of mass and energy, the energy (E) of a quantity of matter is equal to the product of the quantity’s mass (m) and the square of the velocity of light (c).
What does E = mc2 stand for?
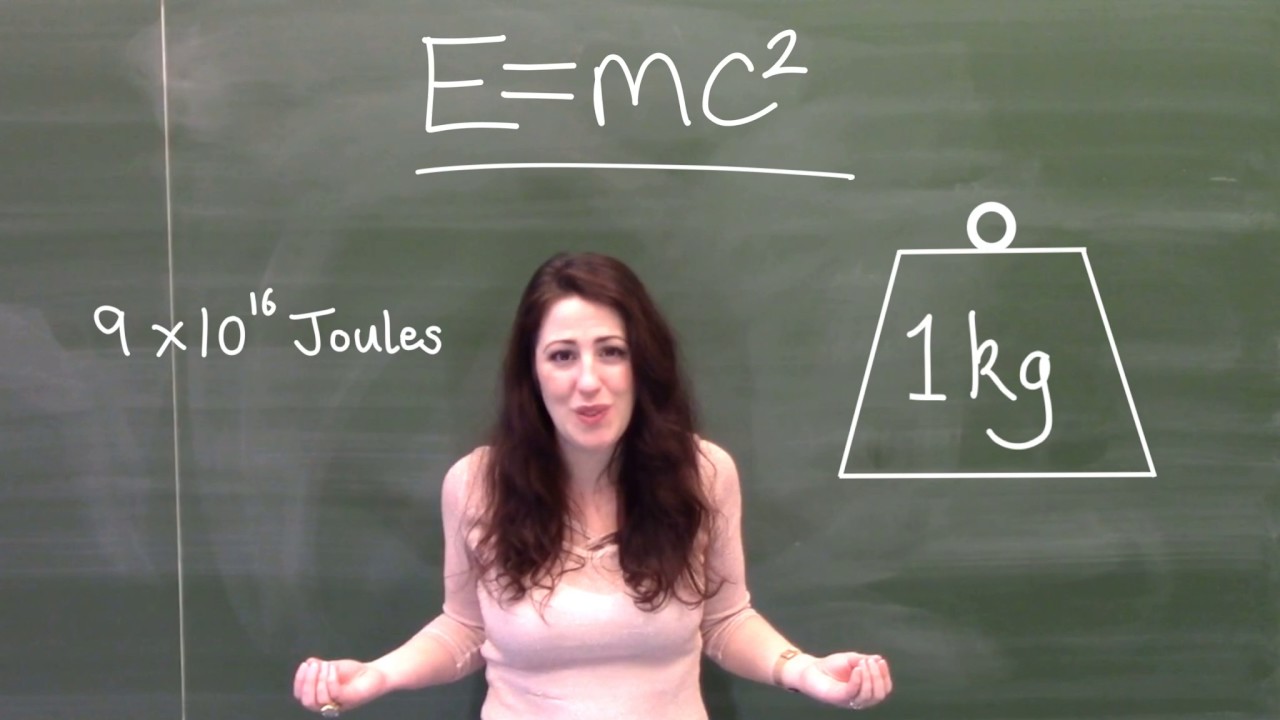
According to Albert Einstein’s law on the equivalence of mass and energy, the energy (E) of a quantity of matter is equal to the product of the quantity’s mass (m) and the square of the velocity of light (c).